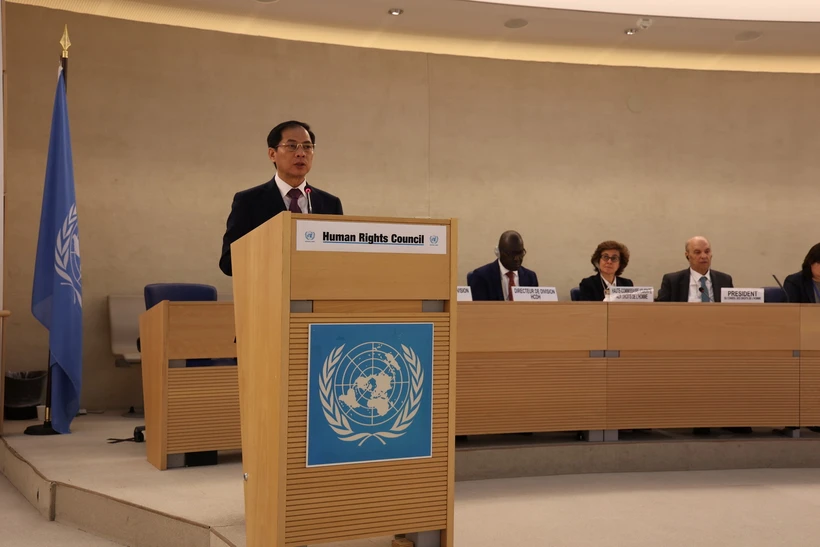
Building, perfecting legal system on human rights
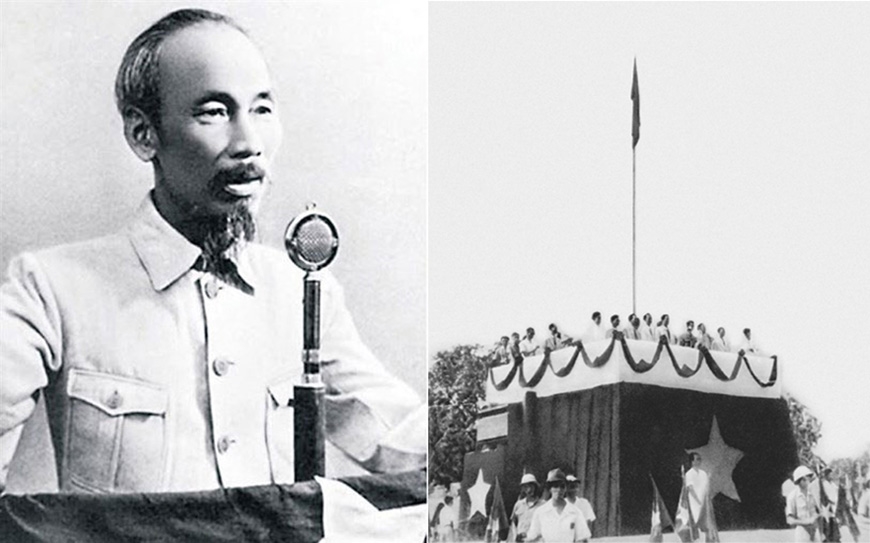

On September 2, 1945, at Hanoi’s Ba Dinh Square, President Ho Chi Minh read the Declaration of Independence giving birth to the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (File photo: VNA)
When President Ho Chi Minh read the Declaration of Independence giving birth to the Democratic Republic of Vietnam in 1945, he affirmed the importance of human rights: “All the peoples of the world are born equal, every nation has the right to life, the right to happiness and the right to freedom”.
Even in its early days, the Vietnamese state built and promulgated many legal documents on human rights, which were also recognised in the 1946 and 1959 Constitutions. In 1957, Vietnam joined four Geneva Conventions of International Humanitarian Law. After becoming a member of the United Nations (UN) in 1977, Vietnam has become even more active and proactive in participating in international conventions on human rights. As of 2022, Vietnam had ratified and joined seven out of nine basic UN conventions on human rights; and ratified and joined 25 conventions of the International Labour Organisation (ILO), including seven out of eight basic conventions.

On October 11, 2022, Vietnam is elected to become a member of the UN Human Rights Council for the 2023-2025 term at the 77th UN General Assembly’s session in New York. (Photo: VNA)
In addition, the state has made great efforts to build a legal system ensuring harmony between national law and international law.
In particular, the 2013 Constitution can be considered the pinnacle of constitutional activities on protecting human rights in Vietnam, affirming the consistency in the issue of human rights and citizen rights mentioned in the Constitutions in 1946, 1959, 1980 and 1992.
Accordingly, the 2013 Constitution (Article 1, Article 2, Article 3) stipulates that the nature of the power of the Vietnamese State is a socialist law-governed state of the people, by the people, and for the people; and the state ensures and promotes the people’s right to mastery, and recognises, respects, protects and ensures human rights and citizen rights.
Providing health check-up and examination and medicince for war veterans, invalids and policies beneficiaries in Lang Son province (Photo: qdnd.vn)
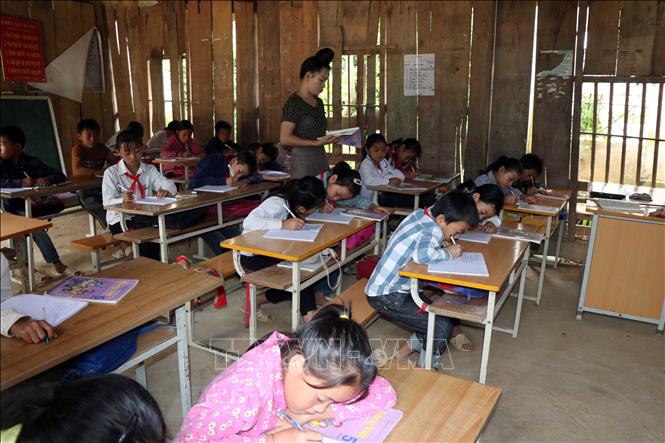

A classroom at Son La province’s boarding school (Photo: VNA)
The 2013 Constitution has 120 articles, with as many as 36 articles stipulating human rights, and basic rights and obligations of citizens. Contents related to human rights are also included in other chapters of the Constitution to create the highest legal basis for all citizens to enjoy, exercise and protect their human rights. The Constitution also sets out duties and responsibilities for state agencies, officials and civil servants to enhance the spirit of social and legal responsibilities in respecting, protecting and ensuring human rights as prescribed by the Constitution.
Ensuring human rights in all fields
With efforts to make and enforce human rights-related laws, Vietnam has gained a lot of remarkable achievements in ensuring human rights in all aspects of social life.
The country has actively implemented the Sustainable Development Goals and increased access to basic services for its people. The social security system has been developed and expanded to benefit more and more people. This can be clearly seen through the increasingly improved quality of social services, especially in the field of employment support, preferential treatment for people who rendered service to the nation as well as improvements in education, health care, housing, and clean water access, especially in remote, mountainous, and island areas.
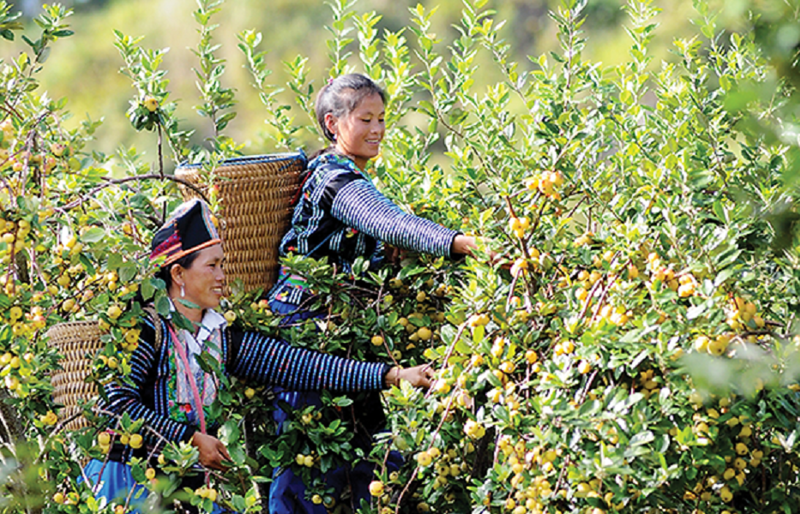

Women in Nam Long hamlet, Hang Chu commune, Bac Yen district, Son La province harvest hawthorn berries (Photo: VNA)
In the latest multidimensional poverty reduction report published by the UN Development Programme (UNDP) in mid-2022, Vietnam was recognised as having achieved much progress in multidimensional poverty reduction thanks to efforts to create jobs, improve social services and expand the social insurance system. Previously, the UNDP also appreciated Vietnam in reducing extreme poverty from the peak rate of about 40% in the 1990s to less than 5% in 2020.
Regarding the right to freedom of belief and religion, Vietnam has built a solid legal framework to ensure this right with the 2013 Constitution and the 2016 Law on Belief and Religion, thus creating favourable conditions for religious activities.
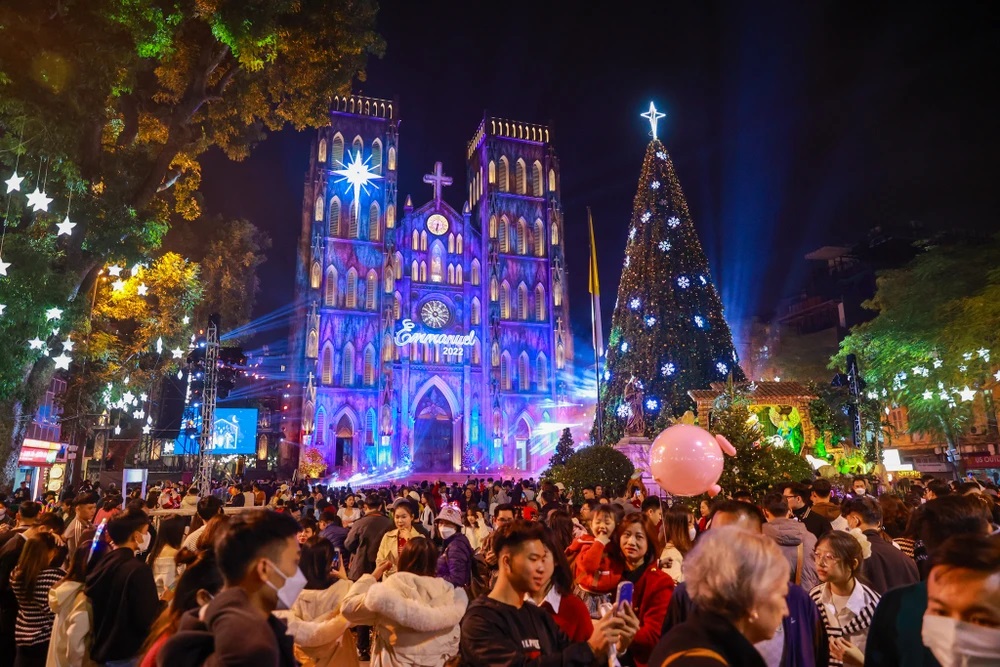

Hanoi people welcome Christmas (Photo: VNA)
The country has also gained achievements regarding the right to freedom of access to the internet, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, and freedom of use of social networks, with about 70 million Vietnamese people using the Internet today. As of the end of 2022, the country had more than 800 press agencies, including 127 newspapers, 670 magazines and 72 radio and television agencies.

Foreign reporters working at the 13th National Party Congress’s Press Centre (Photo: VNA)
According to the Department of Gender Equality under the Ministry of Labour, Invalids and Social Affairs, last year, Vietnam ranked 60th in the world, fourth in Asia and first in the ASEAN Inter-Parliamentary Assembly (AIPA) in terms of the proportion of women participating in people-elected bodies. It ranked third in ASEAN and 47th out of 187 countries participating in the ranking of gender equality in politics and governance. In the economic field, women have the same labour and employment opportunities as men, and women are even given priority in some fields such as education and health. The rate of businesses owned by women reached 26.5%, ranking ninth out of 58 countries and economies participating in the survey.
Actively participating in promoting human rights around the world
Not only has Vietnam gained many achievements in ensuring human rights, it also actively and proactively contributes to promoting and protecting human rights in the region and the world.
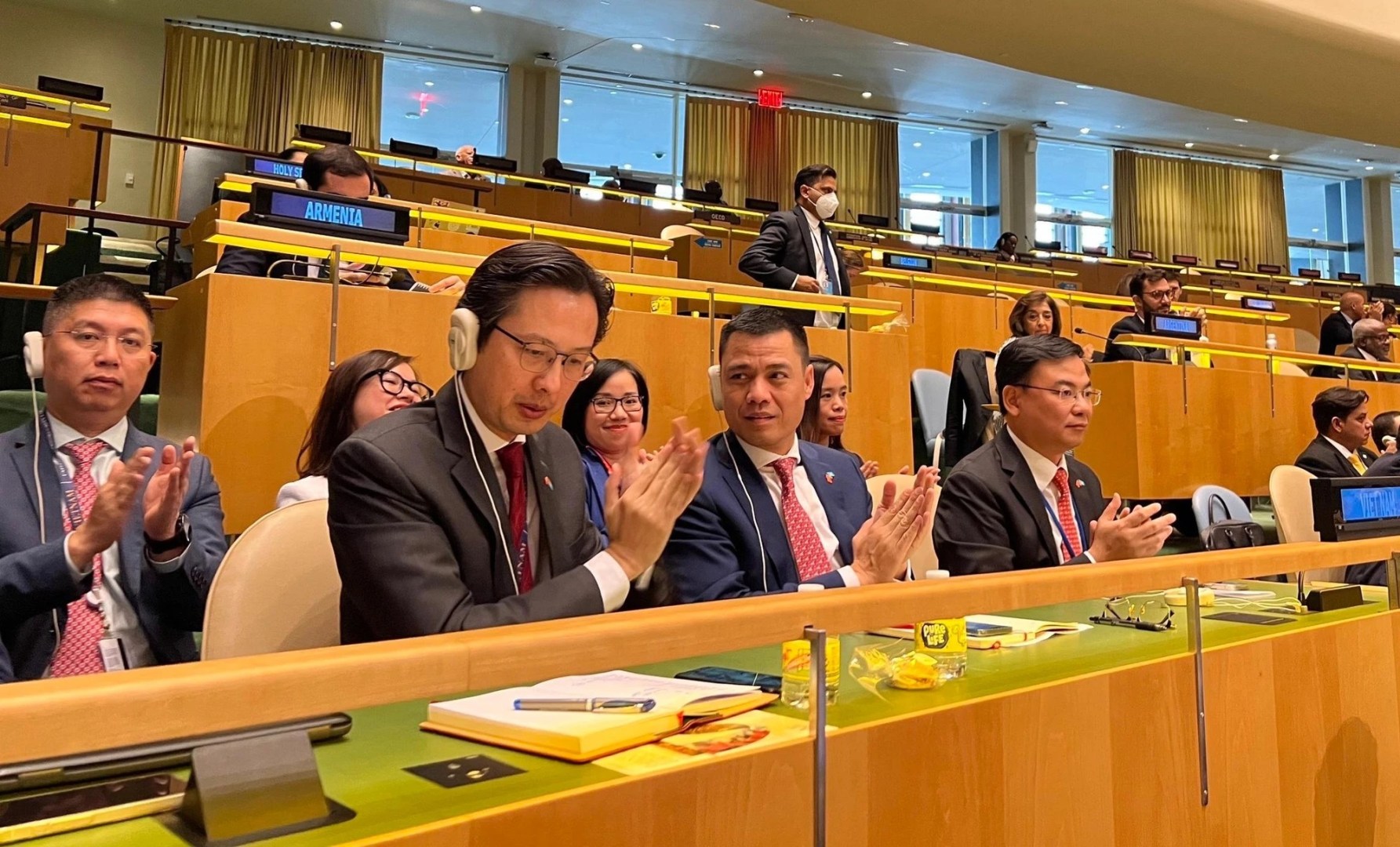
This is clearly shown through the high level of trust of countries when electing Vietnam to the UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC) for the 2023-2025 term and as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council in the 2019-2021 tenure.
Previously, in the 2014-2016 period, Vietnam successfully served as a member of the UNHRC, contributing to protecting national interests, enhancing the position and prestige of the country, and boosting cooperation and dialogue among countries to promote a balanced, progressive, people-oriented approach.
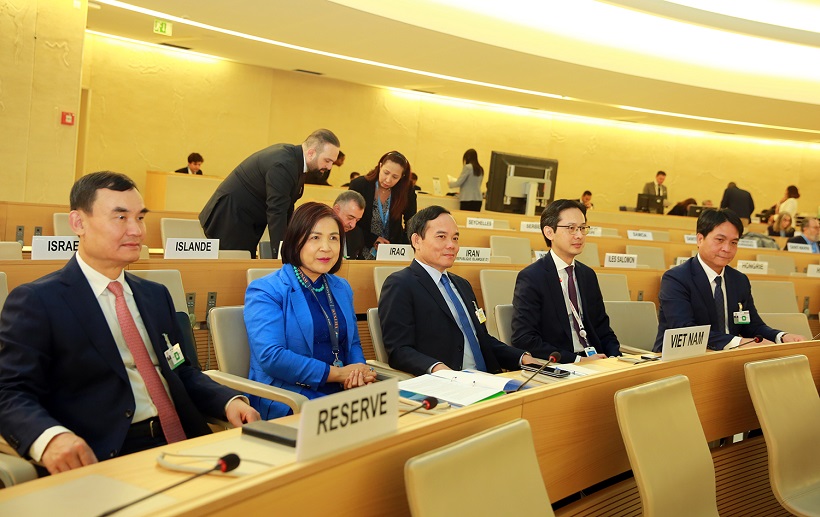

Vietnamese delegation attending the High-Level Segment of the 52nd session of the UN Human Rights Council on February 27, 2023 (Photo: VNA)
In the region, Vietnam’s reputation is demonstrated through its role as Chair of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) as well as Chair of the ASEAN Intergovernmental Commission on Human Rights (AICHR) in 2020.
The 13th National Party Congress in 2021 determined that the people are the centre and subject of the reform process; and all guidelines and policies must truly have their origin in the lives, aspirations, legitimate rights and interests of the people, and take their happiness and prosperity as the goal to strive for. These are the sound and important directions for Vietnam to continue building and perfecting its policies and laws, and protecting and ensuring human rights in the coming years./.
Q.Hoa t.h / VNA


.jpg)







